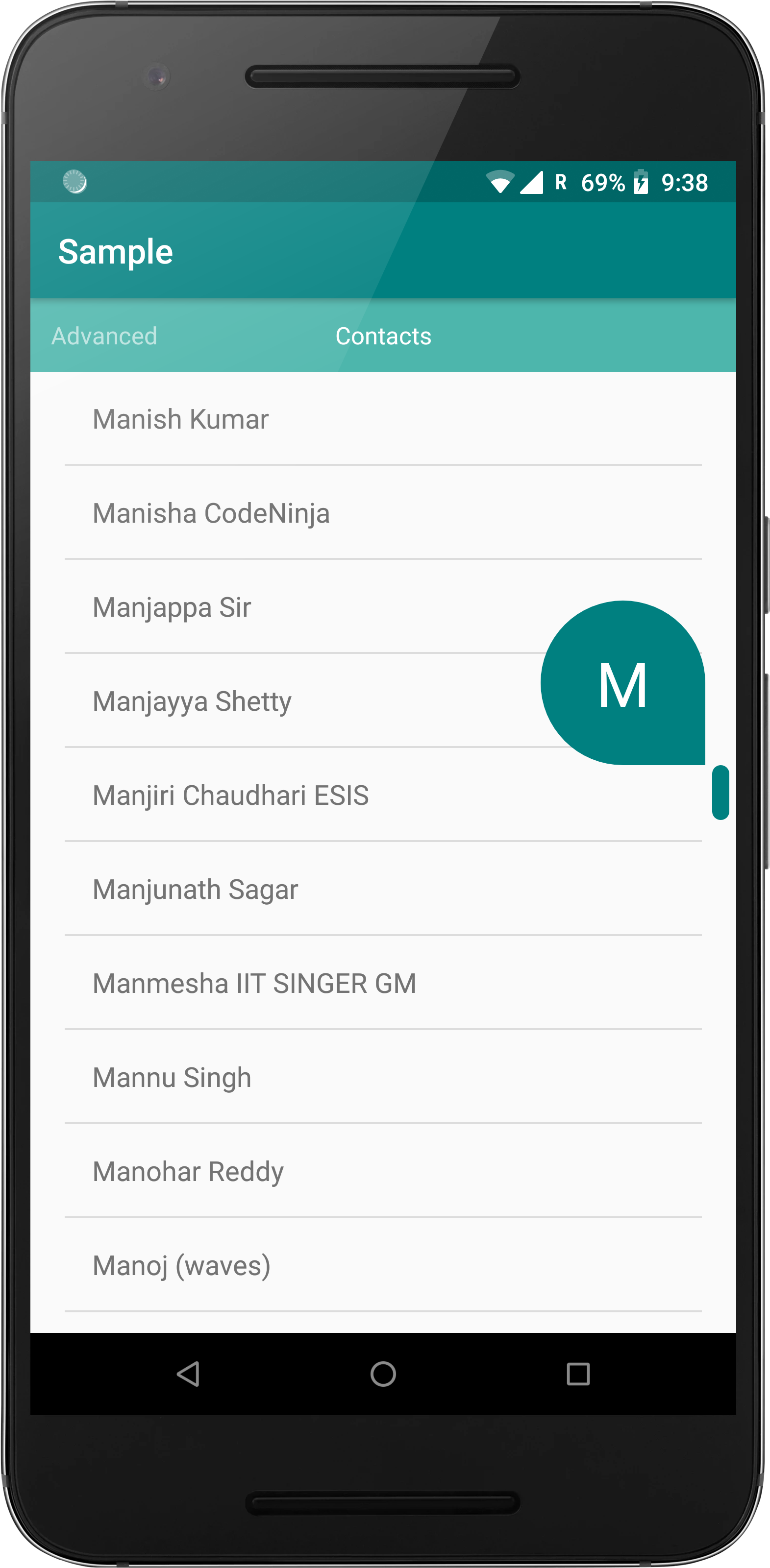
A simple, easy to use and configurable fast scroller for RecyclerView
implementation 'com.quiph.ui:recyclerviewfastscroller:1.0.0'As Kotlin compiles to Java, there's no need to externally add the Kotlin runtime or any other Kotlin dependencies when using this. Also the library is 100% compatible with Java and requires no migration of the base project to Kotlin.
The base layout type for this fast scroller is a RelativeLayout so creating a simple
vertical fast scroller is as simple as adding elements as children to the RecyclerViewFastScroller layout tag
<com.qtalk.recyclerviewfastscroller.RecyclerViewFastScroller
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/fastscroller"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
....
other view tags can also come here
....
</com.qtalk.recyclerviewfastscroller.RecyclerViewFastScroller>Since the fast scroller extends a RelativeLayout other view tags can also be added to it, with the rule being that
the RecyclerView on which the fast scroller functionality needs to be added be the first element in the ViewGroup
If the RecyclerView to be added to the fast scroller is not available during layout creation time, the same can be done programmatically
by calling the attachFastScrollerToRecyclerView method on the RecyclerView
To reflect the item on the index of the top-most visible item, make the adapter implement the OnPopupTextUpdate interface, which overrides the method
onChange(int index) which passes the index of the element whose info needs to be displayed in the popup.
The CharSequence to be displayed should be returned in this method.
Ex:
class MyAdapter : RecyclerView.Adapter<SomeViewHolder>, OnPopupTextUpdate{
// ....
override fun onChange(position: Int): CharSequence {
val header = // compute value for header using position
return header
}
}To get the callback from the fast scroller for different states, a listener can be added using the setHandleStateListener which accepts an interface of type
HandleStateListener which has the following callback methods:
onEngaged- Called when the fast scroller is engagedonDragged- Called on every movement of the fast scroller, note: this does not get called when the handle moves programmatically, i.e when then the Scroll is programmaticonReleased- Called when the fast scroller is released.
trackDrawable- Adds a custom drawable to the scrolling track, defaults tonullhandleDrawable- Adds a custom drawable to the scrolling handle of the fast scrollerpopupDrawable- Adds a custom drawable to the popup used to show the index of the element fast scrolled atpopupTextStyle- Sets the style for the popup text shownfastScrollEnabled- Boolean flag to enable/ disable the fast scroller, the fast scroller view and track are hidden when disabledpopupPosition- An enum to define where the popup should be shown for the fast scroller, one ofbeforeTrack- Positions the popup to be shown before the scroll trackafterTrack- Position it after the scroll track
handleWidth- Use to custom set the width of the fast scroll handle - Defaults to 18dphandleHeight- Use to custom set the height of the fast scroll handle - Defaults to 18dpaddLastItemPadding- By default the last item of theRecyclerViewassociated with the fast scroller has an extra padding of the height of the first visible item found, to disable this behaviour set this asfalsesupportSwipeToRefresh- To support smooth scrolling for RecyclerViews nested within aSwipeRefreshLayouttrackMarginStart- Adds a start margin to the track of the fastscrollertrackMarginEnd- Adds a end margin to the track of the fastscrollerhandleVisibilityDuration- Adds an option to specify the duration to hide the fastscroller handle, defaults to -1, which doesn't hide ithandleHasFixedSize- TODO - currently setting this to false doesn't do anything, as the size of the handle is independent of the item countfastScrollDirection- TODO - currently the fast scroller only works in theverticaldirection
- Different color popups can be shown based on the position of the item shown, to do this, implement the
OnPopupViewUpdatewhich overrides theonUpdate(position: Int, popupTextView: TextView)which return void, but has an instance of theTextViewused in popup, this can be used to change the background.
Check the sample file AdvancedFragment and AdvancedAdapter for example usage
Ex:
class MyAdapter : RecyclerView.Adapter<SomeViewHolder>, OnPopupViewUpdate{
override fun onChange(position: Int, popupTextView: TextView) {
// Do something with the TextView here
popupTextView.background = Color.RED // change some values etc
}
}The popupDrawable attribute and the popupTextStyle attributes can be used to create different kinds of elements, shapes and text appearance combinations, for example like the popup similar to the Google Dialer app:
Check the sample to view the implementation. Many such shapes and text styles can be created.
There is no need for any additional proguard rules when using this.
Thank you for your interest :)
To start contributing, you can check out the issues section with the tag "Good first issue" to start working on the low-hanging fruits. Once you feel comfortable to contribute, fork the project and raise a PR, we'd be happy to review it <3
Our team follows the GitHub pull request workflow: fork, branch, commit, pull request, review, merge. If you're new to GitHub, check out the official guides for more information.
An example commit message summary looks like, For #5: Upgrade gradle to v1.3.0.
Please follow these guidelines for your pull requests:
- All Pull Requests should address an issue. If your pull request doesn't have an
issue, file it!
- GitHub search defaults to issues, not PRs, so ensuring there is an issue for your PR means it'll be easier to find
- The commit message summary should briefly describe what code changed in the commit, not
the issue you're fixing.
- We encourage you to use the commit message body to elaborate what changed and why
- Include the issue number in your commit messages. This links your PR to the issue it's
intended to fix.
- If your PR closes an issue, include
Closes #...in one of your commit messages. This will automatically close the linked issue more info. - If your PR has to go through a longer process, for example QA verification, use the
For #...syntax to allow the linked issue to be closed at a later, more appropriate time.
- If your PR closes an issue, include
- Prefer "micro commits".
- A micro commit is a small commit that generally changes one thing. A single Pull Request may comprise of multiple incremental micro commits.
- A series of micro commits should tell a story. For example, if your goal is to add a new icon to the toolbar, you can make a commit to add the icon asset and then make a commit to use the icon in the code.
- Commits should generally not undo the work of previous commits in the same PR.
- If you're not comfortable making micro commits, it's okay to begin contributing without them.
- Add a reviewer to ensure someone sees, and reviews, your pull request so it can be merged
- If the tests fail, please try to fix them! Keeping the tests passing ensures our code isn't broken and the code is unlikely to get merged without passing tests. If you run into trouble, ask for help!
- If there are UI changes, include a screenshot so UX can also do a visual review
- When in doubt, look at the closed PRs in the repository to follow as an example or ask us online!
If your code is not approved, address the suggested comments, push your changes, and re-request review from your reviewer again.
After your code has been approved and the tests pass, your code will be merged into master by the core team. When merging, we use GitHub's "Rebase and merge":
- We keep a linear git history for readability
- We prefer incremental commits to remain in the history
- It's easier to read, helps with bisection, and matches repo state during review.### Building the source:
To build the aar using using gradle, simply run the build command, ./gradlew build this will build and place the aars in the outputs/aar folder inside the library
module. The final path may look something like:
"${rootProject.projectDir}/recyclerviewfastscroller/build/outputs/aar"This path has a number of aars in it, (debug and release variants namely). To use these aars in the sample, simple uncomment the following line in build.gradle for sample
// implementation files("${rootProject.projectDir}/recyclerviewfastscroller/build/outputs/aar/recyclerviewfastscroller-release.aar")Don't forget to comment the project/ module dependency above it. Re-sync the project and run the sample to test how the compiled version would behave.
We will be using the Nexus Software Repository for pushing our aars to maven-central, there are different methods to do this, another simple way is to upload to bintray and then push to maven-central from there, which one to use can completely depend upon the developer.
Detailed explanation here.
Once the environment is setup as mentioned in the gist, run the following command:
./gradlew clean build uploadArchives- Add support for
horizontalfast scrolling - Make handle size flexible to item count in adapter
- Fix 0 item bug, which makes the fast scroller visible