This library provides 1 line access to common Google Cloud Storage functions. It also provides examples of accessing Google Cloud Storage via the Google APIs Client Library for Java (see the source).
To get started, you'll need to enable Google Cloud Storage on a project and enable authentication via a Service Account.
(This process is a little cumbersome, but it gets easier from here)
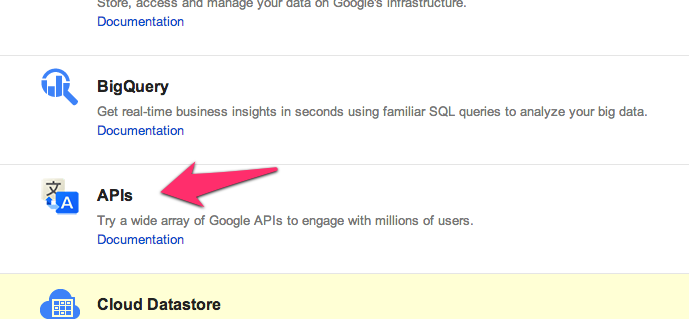
Step 1: From the Google Cloud Console, click the "APIs" link
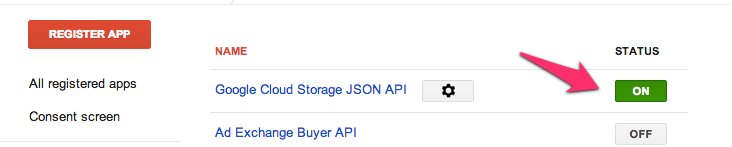
Step 2: Make sure "All" is selected, then click the toggle switch to enable "Google Cloud Storage JSON API"
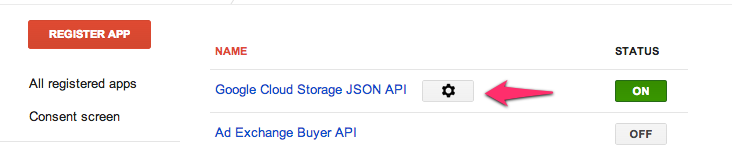
Step 3: Click the Gear next to "Google Cloud Storage JSON API" to access the Google APIs configuration page
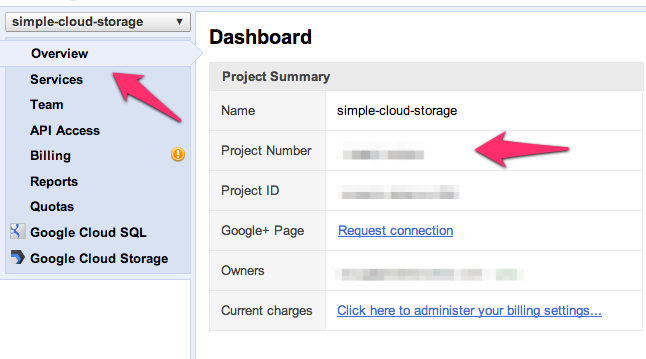
Step 4: In the left menu click "Overview" and note the "Project Number" (needed for later configuration)
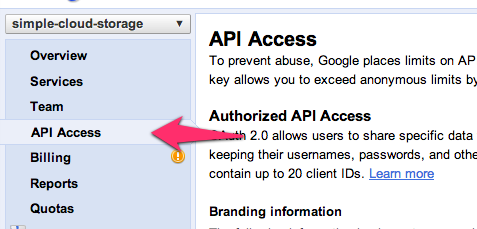
Step 5: In the left menu, select "API Access"
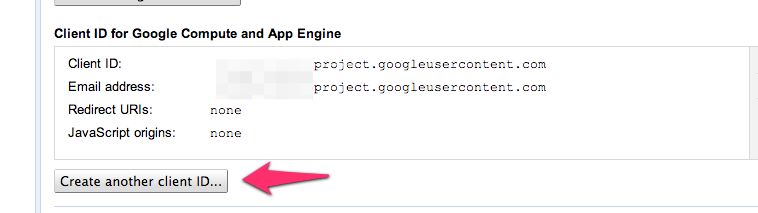
Step 6: Under "Client ID for Google Compute and App Engine", select "Create another Client ID..."
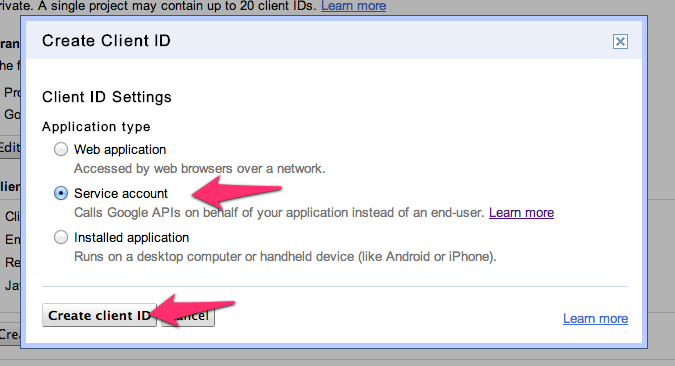
Step 7: Select "Service Account", then click "Create client ID"
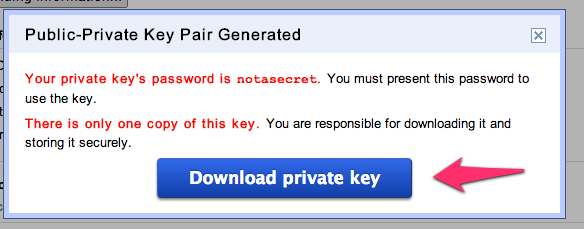
Step 8: Click the "Download private key" button to save the private key (path needed for later configuration)
Step 9: Under Service Account, note the "Client ID" (needed for later configuration)
The credentials created above now need to be added to a properties file so that the library can access your Google Cloud Storage account
- Copy src/main/resources/sample-cloudstorage.properties to a new file named cloudstorage.properties
- Edit the file to use the Project ID, Account ID, and Private Key Path noted above. The Application Name can be anything that makes sense to you (I use the Project Name)
NOTE: cloudstorage.properties needs to be in the root of the classpath. If you leave it in src/main/resources, it will work, but the credentials will be embedded in your jar. Just something to be aware of since there are possible security concerns.
To build the jar you will need to have maven installed. Once that's done, just cd to the project directory and run:
mvn clean install
This will run the unit tests, which will verify that credentials that you configured above are correct.
Once the build is complete the compiled jar can be found in the target directory.
(Finally to the easy part)
package com.pliablematter.cloudstorage;
import java.util.List;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CloudStorage.createBucket("my-bucket");
CloudStorage.uploadFile("my-bucket", "/var/uploads/some-file.txt");
CloudStorage.downloadFile("my-bucket", "some-file.txt", "/var/downloads");
List<String> buckets = CloudStorage.listBuckets();
List<String> files = CloudStorage.listBucket("my-bucket");
}
}