Playing around with CNNs (TF) for Kaggle competition Labeled Faces in the Wild 2017.
There are 3 approaches that have been tested:
-
The first one consists in building a CNN in TensorFlow from scratch (not using any of the pre-trained models). This works good (Kaggle final F-score: 0.957).
-
The second one consists in performing transfer learning on a pre-trained Inception v3 model trained with ImageNet and evaluate if it performs well on a Face Recognition task. This does not perform well (Not submitted to Kaggle).
-
The third one consists in taking an already trained FaceNet system to extract important embeddings of an aligned face and train a SVM that classifies the training embeddings in order to perform inference with test embeddings (that will be obtained from test faces). This works better than 1 (Kaggle final F-score: 0.988).
The competition data can be found under the directory data/.
Dependencies:
- Tensorflow >= 1.4
The first step is to write a model in TensorFlow, which is wrapped in the function cnn_model_fn in the script train.py. This script can be used both to train and evaluate a model specifying a percentage of the training data that will be used to validate the model. When you have a model that works good on this data, you should train without validation in order to take profit of all the training data available. Also, data augmentation can be done (but it is not specified as script arguments, so you will have to modify the script train.py), and it consists on rotating the images [-r, r] and randomly flipping the images.
You can train and validate the existing model by changing your current directory to the root of this project and executing the line:
$ python3 train.py data/X_train.npy data/y_train.npy --validate --validation_split_size 0.2
if by the time it is going to start to train the model and it shows an error like this:
NotFoundError (see above for traceback): Key batch_normalization_3/beta not found in checkpoint [[Node: save/RestoreV2 = RestoreV2[dtypes=[DT_FLOAT, DT_FLOAT, DT_FLOAT, DT_FLOAT, DT_FLOAT, ..., DT_FLOAT, DT_FLOAT, DT_FLOAT, DT_FLOAT, DT_INT64], _device="/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0"](_arg_save/Const_0_0, save/RestoreV2/tensor_names, save/RestoreV2/shape_and_slices)]]
it is because you have trained a model before with different net structure, and it fails to be loaded. If you want to train a different, model, you will have to either rename the model you trained before or delete it. In order to perform fast experiments, you can use the script clear_ckpts.sh in order to delete previously trained models. In that case, you will be executing this line:
$ sh clear_ckpts.sh; python3 train.py data/X_train.npy data/y_train.npy --validate --validation_split_size 0.2
Note: Since this training is made from scratch, the use of CUDA with TF is highly recommended in order to speed up training by several orders or magnitude.
If you think that your model is good enough, you can then train it from scratch using all the training data available:
$ sh clear_ckpts.sh; python3 train.py data/X_train.npy data/y_train.npy
Once you have trained your model using all the training data, you can find it under faces_convnet_model/. Then, you are ready to make the ineference of the test set data/X_test.npy, generate the csv file as it is specified in the kaggle page of the competition. All this can be done (if you have the trained model under faces_convnet_model/) by executing:
$ python3 infer_test_and_create_submission_file.py data/X_test.npy
This will create your submission file submission.csv, ready to be uploaded to Kaggle. My best score with this approach is 0.95031 F-score in the Kaggle Public test split and 0.95652 in the Kaggle Private test split.
https://i.gyazo.com/e383d8ffbd16e498c95cd269340144e0.png
Dependencies:
- TF Slim. If you have errors or issues wrt slim (cannot import models or slim is not found), try this.
This method uses tfrecord extension to work with data. The script that builds the tfrecord from the data can be found in KaggleLFW17/data_conversion, and it is named as faces_dataset_from_jpg_to_tfrecord.py
[...]
This part of the README is Work In Progress, since this method did not perform well on the task of Face Recognition. And will only explained for didactic purposes
Method 3. ImageNet (Inception-Resnet v1) trained on VGGFace2 with softmax loss and MTCNN for face alignment (pre-processing)
Dependencies:
- Tensorflow >= 1.7
Note: To keep this simple, only the training and the submission is explained.
- Convert .npy data to .jpg files stored under a parent directory
lfw. The pictures of each class will be stored under the correspondent directory (i.e.lfw/0/for person 0,lfw/1/for person 1, ..., andlfw/6/for person 6). I recommend you to do this under the/tmp/folder:
$ python3 data_conversion/faces_dataset_from_npy_to_jpg.py --mode TRAIN
This script will also perform Data Augmentation. After this, you will have the folder /tmp/lfw17/faces_photos, that will contain the training data organised in each of the folders that hold the images of each class.
- Align images after Data Augmentation by using MTCNN:
$ python3 facenet/src/align/align_dataset_mtcnn.py \
/tmp/lfw17/faces_photos \
/tmp/lfw17/faces_photos_mtcnnpy_182 \
--image_size 182 \
--margin 44
-
Download FaceNet model checkpoint (Inception-Resnet v1 trained on VGGFace2) to calculate embeddings. Unzip the model and put it under
/KaggleLFW17/facenet/src/models/so the folder20180402-114759/that contains the model and the checkpoint is under the foldermodels/. -
(Train SVM with embeddings as features. Use 200 images of each class for training, and the other data will be the validation split:
$ python3 facenet/src/classifier.py TRAIN \
/tmp/lfw17/faces_photos_mtcnnpy_182 \
facenet/src/models/20180402-114759/20180402-114759.pb \
facenet/src/models/lfw_classifier.pkl \
--batch_size 32 \
--min_nrof_images_per_class 1 \
--nrof_train_images_per_class 200 \
--use_split_dataset
Output:
Number of classes: 7
Number of images: 1333
Loading feature extraction model
Model filename: facenet/src/models/20180402-114759/20180402-114759.pb
Calculating features for images
Training classifier
Saved classifier model to file "facenet/src/models/lfw_classifier.pkl"
- Evaluate (TODO: 1. separate tr and eval datasets; 2. Remove extra folders that make CLASSIFY mode think that there are 2 more classes despite there is no impact on accuracy)
python3 facenet/src/classifier.py CLASSIFY \
/tmp/lfw17/faces_photos_mtcnnpy_182 \
facenet/src/models/20180402-114759/20180402-114759.pb \
facenet/src/models/lfw_classifier.pkl \
--batch_size 32
Output:
Number of classes: 7
Number of images: 2897
Loading feature extraction model
Model filename: facenet/src/models/20180402-114759/20180402-114759.pb
Calculating features for images
Testing classifier
Loaded classifier model from file "facenet/src/models/lfw_classifier.pkl"
Accuracy: 0.985
- Train the SVM with all the data (assuming you have done the previous train & eval steps, and the images are already augmented and aligned):
$ python3 facenet/src/classifier.py TRAIN \
/tmp/lfw17/faces_photos_mtcnnpy_182 \
facenet/src/models/20180402-114759/20180402-114759.pb \
facenet/src/models/lfw_classifier.pkl \
--batch_size 32
- Convert test data to .jpg images
$ python3 data_conversion/faces_dataset_from_npy_to_jpg.py --mode TEST
This will generate the folder /tmp/lfw17_test/faces_photos with the test data (obviously the data is not organized in folders, as we do not know the class of each image).
- Align (preprocess) test images, as we did in the training procedure:
$ python3 facenet/src/align/align_dataset_mtcnn.py \
/tmp/lfw17_test/ \
/tmp/lfw17_test/aligned \
--image_size 182 \
--margin 44
This will create the folder /tmp/lfw17_test/aligned/faces_photos, that contains the resized images with the aligned faces that will be recognized.
- Create the submission file using the pretrained model and the trained classifier:
$ python3 facenet/src/submit.py CLASSIFY \
/tmp/lfw17_test/aligned/ \
facenet/src/models/20180402-114759/20180402-114759.pb \
facenet/src/models/lfw_classifier.pkl \
--batch_size 32
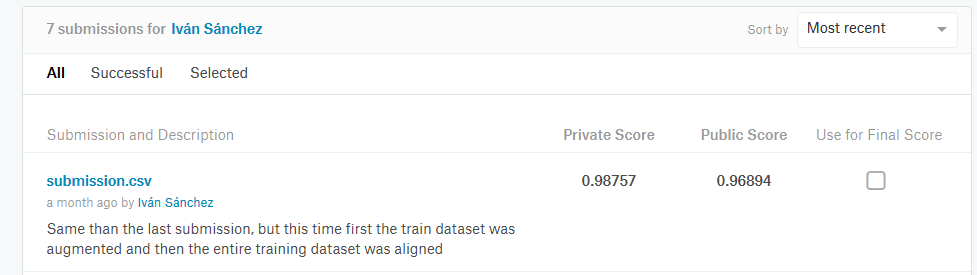
This will create your submission file submission.csv, ready to be uploaded to Kaggle. My best score with this approach is 0.96894 F-score in the Kaggle Public test split and 0.98757 in the Kaggle Private test split.