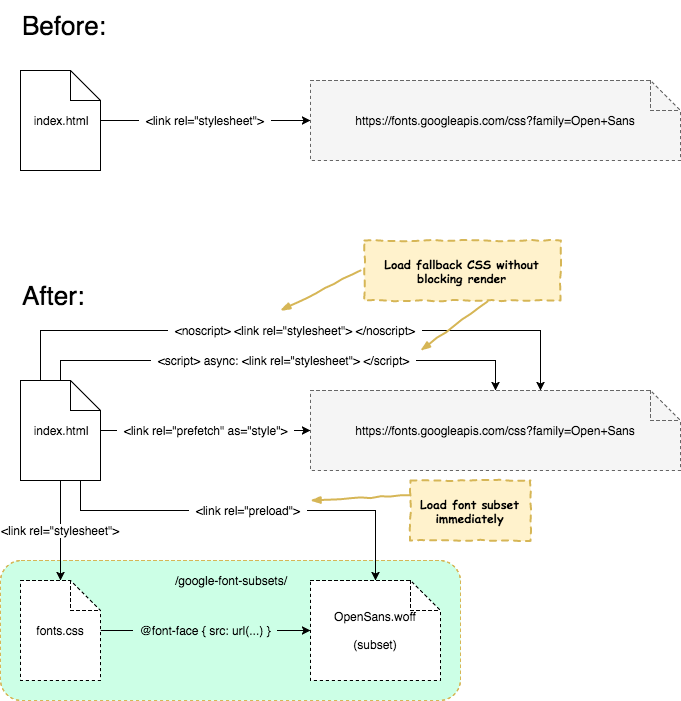
A command line tool to statically analyse your page in order to generate the most optimal web font subsets, then inject them into your page.
Speed up your time to first meaningful paint by reducing the web font payload and critical path to the font files.
Subfont will:
- Automatically figure out what characters are used from each font
- Warn you about usage of characters that don't exist as glyphs in your webfonts
- Create an exact subset of used characters of each font
- Reduce the variation space of variable fonts based on the actual usage (when the
--instanceswitch is used) - Generate web fonts in both
woff2andwoffformats - Add preload hints for the subsets to reduce time to first meaningful paint
- Give the subsetted fonts new names and prepend them in front of the original fonts in your
font-familydefinitions (enables missing glyph fallback) - Async load your original
@font-facedeclaring CSS at the bottom of your page, moving it off the critical path
Currently supported font services:
- Google fonts
- Local fonts
If you know of font services with liberal font usage licenses, open an issue and we'll add support for them
Get the basic CLI tool, which supports subsetting Google Fonts and optimizing all local fonts with preloading instructions:
npm install -g subfont
Run subfont on the files you are ready to deploy to a static file hosting service. If these are build artifacts from another build system, and not the original files, run subfont path/to/artifacts/index.html -i to have subfont clobber the dist files in their original location.
If you want to run directly against your raw original files, it is recommended to create a recursive copy of your files which you run subfont on. This keeps your original authoring abstraction unchanged.
If you have a use case where the automatic tracing doesn't find all the characters you need, you can tell subfont to include specific characters in the subsets by adding a custom -subfont-text property to the respective @font-face declarations.
Example where all numerical digits are added to the bold italic Roboto variant:
@font-face {
font-family: Roboto;
font-style: italic;
font-weight: 700;
src: url(roboto.woff) format('woff');
-subfont-text: '0123456789';
}An easier, but less fine-grained option is to use the --text switch to include a set of characters in all created subsets.
You can have subfont output a copy of your input files to a new directory. This uses Assetgraph to trace a dependency graph of your website and writes it to your specified output directory. Be aware of any errors or warnings that might indicate Assetgraph having problems with your code, and be sure to double check that the expected files are in the output directory. Run subfont path/to/index.html -o path/to/outputDir.
You can also have subfont scrape a website directly using http and write the output to local disk. This use is likely to fail in a number of ways and should mostly considered a demo feature if you just want to give the tool a quick go to see what it will do to your page. Run subfont https://yourpage.me -o path/to/outputDir.
$ subfont --help
Create optimal font subsets from your actual font usage.
subfont [options] <htmlFile(s) | url(s)>
Options:
--help Show help [boolean]
--version Show version number [boolean]
--root Path to your web root (will be deduced from your input files
if not specified) [string]
--canonical-root, --canonicalroot URI root where the site will be deployed. Must be either an
absolute, a protocol-relative, or a root-relative url[string]
--output, -o Directory where results should be written to [string]
--browsers Override your projects browserslist configuration to specify
which browsers to support. Controls font formats and
polyfill. Defaults to browserslist's default query if your
project has no browserslist configuration [string]
--formats Font formats to use when subsetting. The default is to select
the formats based on the browser capabilities as specified
via --browsers or the browserslist configuration.
[array] [choices: "woff2", "woff", "truetype"]
--text Additional characters to include in the subset for every
@font-face found on the page [string]
--fallbacks Include fallbacks so the original font will be loaded when
dynamic content gets injected at runtime. Disable with
--no-fallbacks [boolean] [default: true]
--dynamic Also trace the usage of fonts in a headless browser with
JavaScript enabled [boolean] [default: false]
--in-place, -i Modify HTML-files in-place. Only use on build artifacts
[boolean] [default: false]
--inline-css Inline CSS that declares the @font-face for the subset fonts
[boolean] [default: false]
--font-display Injects a font-display value into the @font-face CSS.
[string] [choices: "auto", "block", "swap", "fallback", "optional"] [default: "swap"]
--recursive, -r Crawl all HTML-pages linked with relative and root relative
links. This stays inside your domain
[boolean] [default: false]
--relative-urls Issue relative urls instead of root-relative ones
[boolean] [default: false]
--instance Experimentally instance variable fonts when the variation
space isn't fully used [boolean] [default: false]
--silent, -s Do not write anything to stdout [boolean] [default: false]
--debug, -d Verbose insights into font glyph detection
[boolean] [default: false]
--dry-run, --dry, --dryrun Don't write anything to disk [boolean] [default: false]
https://meowni.ca/font-style-matcher/
MIT