In this guide, we’ll build a decentralized application (dApp) on Linea, an Ethereum Layer 2 solution using zero-knowledge proofs. We’ll create a simple prediction market for ETH/USD price. By the end, you will learn:
- The fundamentals of zkEVMs and Linea
- How to build a prediction market dApp using an oracle like API3
- How to deploy Solidity smart-contracts on Linea Sepolia using Atlas.
- Bonus: How to build a front-end using MetaMask for your dApp
- Basic knowledge of Solidity
- Sepolia ETH on Linea Sepolia Testnet. If you have an Infura acccount, get some here
- MetaMask browser extension installed
- (Optional) Basic Knowledge of JavaScript/HTML and Node.js or Python installed
zkEVMs (Zero-Knowledge Ethereum Virtual Machines) are scaling solutions that aim to improve Ethereum's transaction speed and reduce costs. They do so by moving the computation and execution of EVM transactions off-chain while verifying their validity on-chain using zero-knowledge proofs. Read more about their powerful properties on Vitalik's blog.
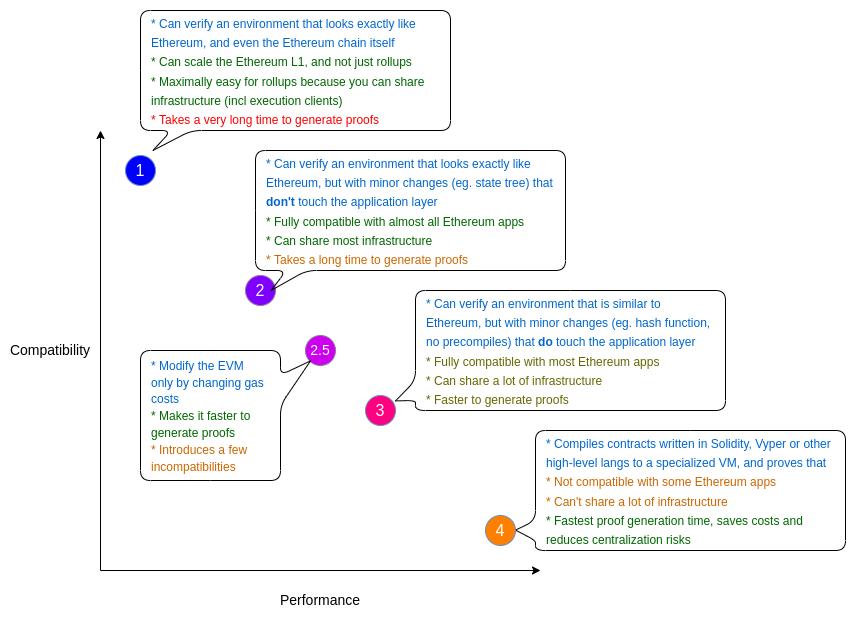
We can distinguish at least four types of zkEVMs by the trade-offs they make between optimizing for performance (speed and cost) or compatibility with the EVM. See the chart below from Vitalik's blog.
For this guide, we will build on Linea. It is a Type 2 zkEVM, which means developers can write, test, compile, deploy, and verify smart contracts using traditional Ethereum tooling (e.g., Hardhat, Foundry, Remix, or Atlas). There are minor differences with Ethereum, which you can find in the Linea Docs.
A prediction market is a type of decentralized application where users can bet on the likelihood of future events. When enough people participate, they can be considered as “social epistemic tools,” insofar as prices in these markets reflect the consensus on the likelihood of specific outcomes, such as election results.
We will build a simple prediction market for the price of Ethereum in Solidity. To retrieve the price of Ethereum, we will use an oracle (API3), which allows the blockchain network to get information about the real world - in our case - ETH price in USD.
The contract allows users to bet on whether Ethereum’s price will go up or down in the next 24h. It uses the modifier OnlyDuringBettingPeriod() and functions startBettingPeriod() and closeBettingPeriod() to control when to open/close the ETH prediction market and to only allow bets during that time.
modifier onlyDuringBettingPeriod() {
require(block.timestamp < startTime + 24 hours, "Betting period over");
_;
}
function startBettingPeriod() external {
startTime = block.timestamp;
startPrice = getLatestPrice();
}
function closeBettingPeriod() external {
require(block.timestamp >= startTime + 24 hours, "Betting period not over");
endPrice = getLatestPrice();
bool priceIncreased = endPrice > startPrice;
emit BetResult(priceIncreased, endPrice);
distributeWinnings(priceIncreased);
}
The price of ETH is obtained using API3, and IPoxy contract interface. The getLatestPrice() function retrieves the latest ETH/USD price from API3's price feed. You can find different oracles on the Linea docs.
function getLatestPrice() public view returns (int224) {
(int224 price,) = priceFeed.read();
require(price > 0, "Failed to retrieve price");
return price;
}
Users can place bets on whether the ETH price will go up or down during the betting period. The contract records each bet with its direction (up or down) and amount wagered in an array.
function placeBet(BetDirection _direction) external payable onlyDuringBettingPeriod {
require(msg.value > 0, "You must bet some ETH");
bets.push(Bet(msg.sender, _direction, msg.value, false));
emit BetPlaced(msg.sender, _direction, msg.value);
}
After the betting period closes, the contract determines which bets were correct and allocates the winnings. It iterates through the Bet array, and, for each bet, checks whether the bet direction matches the outcome (up or down) and whether the bet has already been claimed. If a user’s bet matches the result, they receive twice the amount wagered. Winners can withdraw their earnings after the betting period. The contract checks the user’s balance of winnings and transfers the amount to them.
function distributeWinnings(bool priceIncreased) internal {
for (uint256 i = 0; i < bets.length; i++) {
Bet storage bet = bets[i];
if (
!bet.claimed
&& (
priceIncreased && bet.direction == BetDirection.Up
|| !priceIncreased && bet.direction == BetDirection.Down
)
) {
pendingWithdrawals[bet.better] += bet.amount * 2;
}
bet.claimed = true;
}
}
function withdrawWinnings() external {
uint256 amount = pendingWithdrawals[msg.sender];
require(amount > 0, "No winnings to withdraw");
pendingWithdrawals[msg.sender] = 0;
payable(msg.sender).transfer(amount);
}
receive() external payable {}
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "@api3/contracts/api3-server-v1/proxies/interfaces/IProxy.sol";
contract EthereumPriceBetting {
IProxy internal priceFeed;
enum BetDirection {
Up,
Down
}
struct Bet {
address better;
BetDirection direction;
uint256 amount;
bool claimed;
}
uint256 public startTime;
int224 public startPrice;
int224 public endPrice;
Bet[] public bets;
mapping(address => uint256) public pendingWithdrawals;
event BetPlaced(address indexed better, BetDirection direction, uint256 amount);
event BetResult(bool priceIncreased, int224 endPrice);
// API3 proxy address for Ethereum/USD price feed
address public constant priceFeedAddress = 0xa47Fd122b11CdD7aad7c3e8B740FB91D83Ce43D1;
constructor() {
priceFeed = IProxy(priceFeedAddress);
}
// The betting period now lasts for only 24 hours
modifier onlyDuringBettingPeriod() {
require(block.timestamp < startTime + 24 hours, "Betting period over");
_;
}
function startBettingPeriod() external {
startTime = block.timestamp;
startPrice = getLatestPrice();
}
function closeBettingPeriod() external {
require(block.timestamp >= startTime + 24 hours, "Betting period not over");
endPrice = getLatestPrice();
bool priceIncreased = endPrice > startPrice;
emit BetResult(priceIncreased, endPrice);
distributeWinnings(priceIncreased);
}
function getLatestPrice() public view returns (int224) {
(int224 price,) = priceFeed.read(); // Using API3's `read()` function
require(price > 0, "Failed to retrieve price");
return price;
}
function placeBet(BetDirection _direction) external payable onlyDuringBettingPeriod {
require(msg.value > 0, "You must bet some ETH");
bets.push(Bet(msg.sender, _direction, msg.value, false));
emit BetPlaced(msg.sender, _direction, msg.value);
}
function distributeWinnings(bool priceIncreased) internal {
for (uint256 i = 0; i < bets.length; i++) {
Bet storage bet = bets[i];
if (
!bet.claimed
&& (
priceIncreased && bet.direction == BetDirection.Up
|| !priceIncreased && bet.direction == BetDirection.Down
)
) {
pendingWithdrawals[bet.better] += bet.amount * 2;
}
bet.claimed = true;
}
}
function withdrawWinnings() external {
uint256 amount = pendingWithdrawals[msg.sender];
require(amount > 0, "No winnings to withdraw");
pendingWithdrawals[msg.sender] = 0;
payable(msg.sender).transfer(amount);
}
receive() external payable {}
}
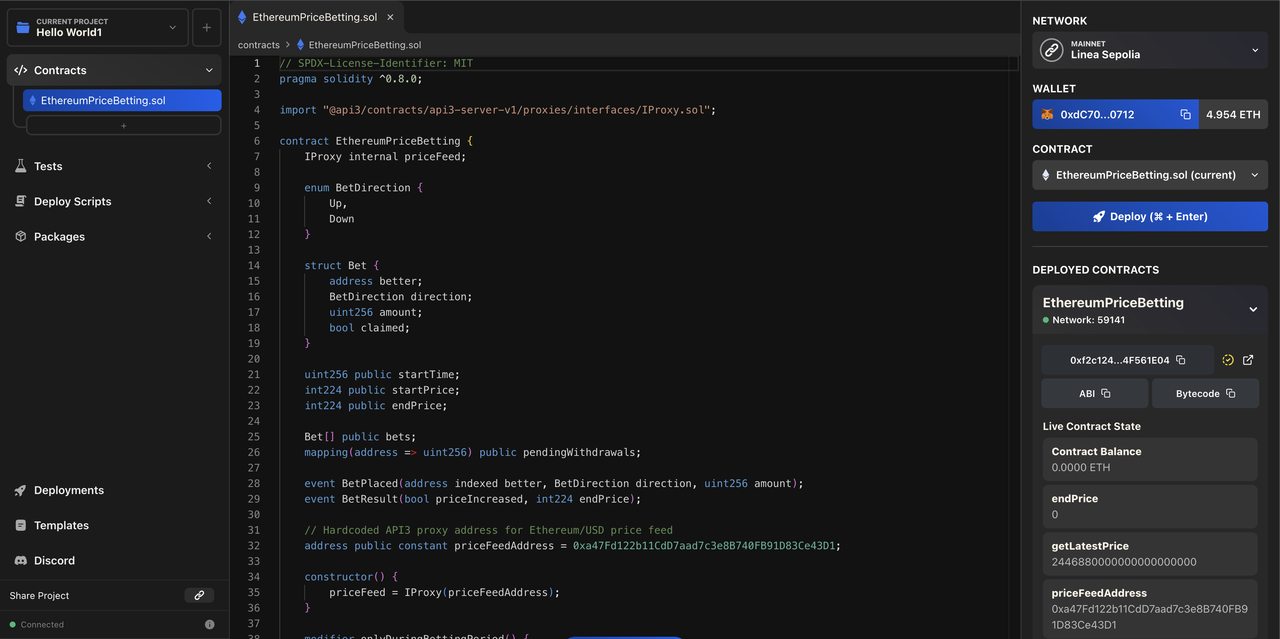
To deploy this contract, we will use Atlas, which is a recent user-friendly IDE. Follow these steps:
- Go to https://app.atlaszk.com/ide
- In the Contracts section, create a new Solidity file called
EthereumPriceBetting.soland paste the full code. - Select “Linea Sepolia” as the network, connect your MetaMask wallet, and switch to the Linea Sepolia Testnet when prompted.
- Click on Deploy. Confirm the transaction in MetaMask to deploy the contract.
Once deployed, you will see the contract details (address, ABI, bytecode) in the Deployed Contracts section. You can now interact with the contract to open/close the betting period, place bets, and withdraw winnings. Note: You'll need to fund the contract so it can pay the winnings.
Congratulations, you have just deployed your very first dApp on Linea Sepolia Testnet!
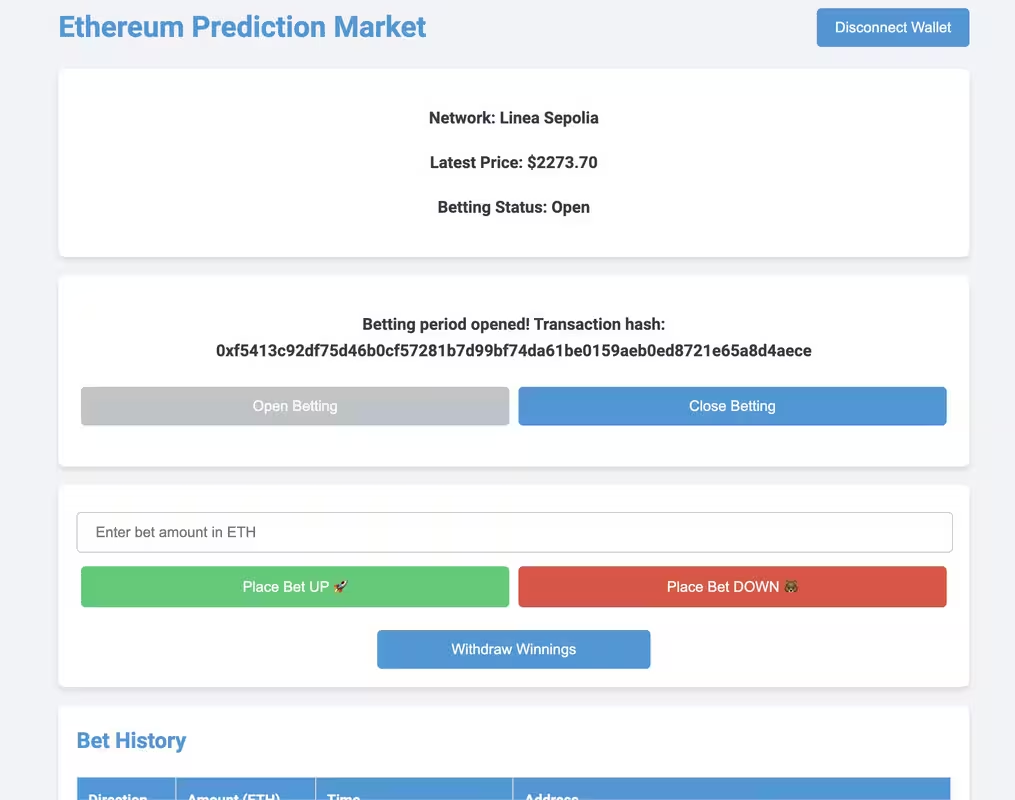
We can build a front-end that connects to a MetaMask wallet to interact with the dApp. The index.html provided in this repo contains a simple interface with buttons, style.css a basic CSS styling, and App.jsa JavaScript code (with ethers.js) to manage the logic between the interface, the MetaMask wallet, and Linea Sepolia Testnet (see below).
App.js handles the key functions to manage MetaMask wallet connection/disconnection and network switching to Linea Sepolia. It imports ethers.js for interacting with Linea Sepolia tesnet.
1. loadContractAbi
This function loads the ABI (Application Binary Interface) of the deployed contract, which is necessary for interacting with the contract on the Linea Sepolia testnet network.
async function loadContractAbi() {
try {
const response = await fetch('contract_abi.json');
return await response.json();
} catch (error) {
updateTransactionStatus('Failed to load contract ABI. Please refresh the page.');
}
}2. connectMetaMask
This function connects the dApp to the MetaMask wallet, initializes the provider, signer, and manages network switching. Note that you can also use the MetaMask SDK
async function connectMetaMask() {
if (typeof window.ethereum !== 'undefined') {
try {
const accounts = await window.ethereum.request({ method: 'eth_requestAccounts' });
provider = new ethers.providers.Web3Provider(window.ethereum);
signer = provider.getSigner();
await signer.getAddress();
updateTransactionStatus('Connected to MetaMask!');
updateConnectButton('Disconnect Wallet', disconnectWallet);
// Check network and switch if needed
const networkId = await window.ethereum.request({ method: 'eth_chainId' });
if (networkId !== lineaSepoliaChainId) {
await switchToLineaSepolia();
} else {
await initializeContract();
}
} catch (error) {
updateTransactionStatus(`Failed to connect to MetaMask: ${error.message}`);
}
} else {
updateTransactionStatus('MetaMask is not installed. Please install it to use this dApp.');
}
}3. switchToLineaSepolia
This function switches the wallet's network to Linea Sepolia
async function switchToLineaSepolia() {
try {
await window.ethereum.request({
method: 'wallet_switchEthereumChain',
params: [{ chainId: lineaSepoliaChainId }]
});
updateTransactionStatus('Switched to Linea Sepolia network.');
// Reconnect the wallet if necessary
const accounts = await window.ethereum.request({ method: 'eth_accounts' });
if (accounts.length > 0) {
await initializeContract();
} else {
await connectMetaMask();
}
} catch (switchError) {
if (switchError.code === 4902) { // Chain not added
await addLineaSepoliaNetwork();
} else {
updateTransactionStatus('Failed to switch to Linea Sepolia. Please switch manually in MetaMask.');
}
}
}
Once you have deployed the contract on the network:
- In the
App.jsfile replaceCONTRACT_ADDRESSwith your freshly deployed dApp address - Create a JSON file named
contract_abi.jsonin the same directory as yourindex.htmlandapp.jsfile - Note: if you deployed to Linea Mainnet, you'll have to change the chainID (in hex), and network RPC (see Linea Network info)
Note: in Atlas you can find both the contract address and ABI in the Deployed Contracts menu.
You can serve the HTML file locally using Node.js with the http-server or express module.
-
First, install http-server globally:
npm install -g http-server -
Navigate to the directory where your index.html file is located:
cd /path/to/your/directory -
Run the server:
http-server -
Open a browser and go to http://localhost:8080 to view your dApp.
You can use Python's built-in http.server to serve the HTML file.
-
Navigate to the directory where your index.html file is located:
cd /path/to/your/directory -
Start a simple HTTP server, for Python 3:
python3 -m http.server 8000 -
Open http://localhost:8000 in your browser to view your dApp.
You can now play around the dApp while using an intuitive front-end.