Refer this link
- Install/Upgrade Docker for Mac 18.03 CE Edition
- Install google-cloud-sdk
- Enable Google Cloud Engine API
- Authenticate Your Google Cloud using
gcloud auth
Make sure that Python 2.7 is installed on your system:
Ajeets-MacBook-Air:~ ajeetraina$ python -V
Python 2.7.10
Download the corresponding version of Google Cloud SDK. In this case the Mac OS version for 64-bits systems is downloaded.
wget https://dl.google.com/dl/cloudsdk/channels/rapid/downloads/google-cloud-sdk-195.0.0-darwin-x86_64.tar.gz
Untar the downloaded file, as follows:
tar xfz google-cloud-sdk-195.0.0-darwin-x86_64.tar.gz
and execute the following command to install Google Cloud SDK in your system:
./google-cloud-sdk/install.sh
gcloud init
In your browser, log in to your Google user account when prompted and click Allow to grant permission to access Google Cloud Platform resources.
gcloud auth login
gcloud container clusters create k8s-lab1 --disk-size 10 --zone asia-east1-a --machine-type n1-standard-2 --num-nodes 3 --scopes compute-rw
You should be able to view GKE cluster under Preference UI by now.
Be aware that your Kubernetes context can be named differently and it depends on the project's name under which the Kubernetes cluster is being deployed.
kubectl get nodes
You can connect to your cluster via command-line or using a dashboard. Remember your project's name can be different.
gcloud container clusters get-credentials k8s-lab1 --zone asia-east1-a --project captain-199803
$ kubectl run nginx --image=nginx --replicas=3
deployment "nginx" created
kubectl get pods -owide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
nginx-7c87f569d-glczj 1/1 Running 0 8s 10.12.2.6 gke-k8s-lab1-default-pool-b2aaa29b-w904
nginx-7c87f569d-pll76 1/1 Running 0 8s 10.12.0.8 gke-k8s-lab1-default-pool-b2aaa29b-2gzh
nginx-7c87f569d-sf8z9 1/1 Running 0 8s 10.12.1.8 gke-k8s-lab1-default-pool-b2aaa29b-qpc7
You can see that each nginx pod is now running in a different node (virtual machine).
$ kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80 --target-port=80 \
--type=LoadBalancer
service "nginx" exposed
kubectl get service nginx
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx LoadBalancer 10.15.247.8 <pending> 80:30253/TCP 12s
It may take several minutes to see the value of EXTERNAL_IP.
If you don’t see it the first time with the above command, retry every minute or so until the value of EXTERNAL_IP is displayed.
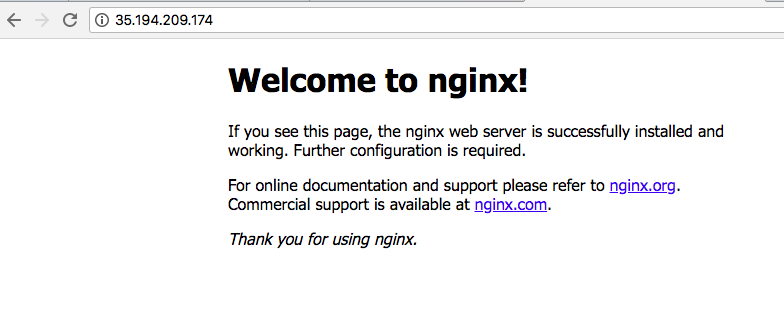
You can then visit http://EXTERNAL_IP/ to see the server being served through network load balancing.
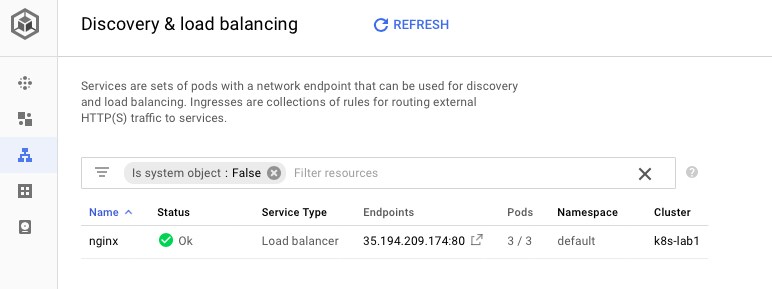
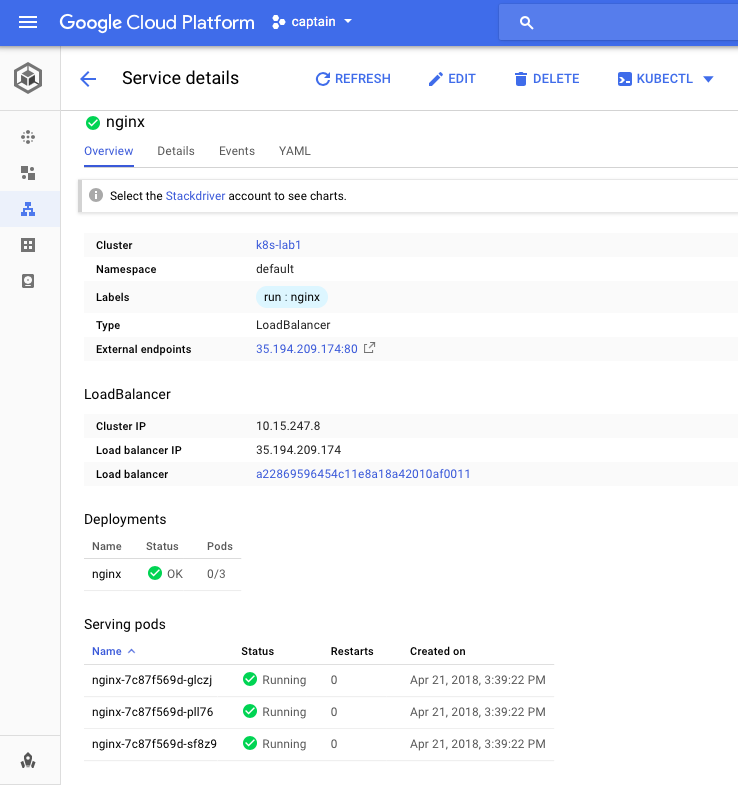
GKE provides amazing platform to view Workloads & Load-balancer as shown below:
GKE also provides UI for displaying Loadbalancer:
gcloud container clusters delete k8s-lab1 --zone asia-east1-a