A curated list of awesome threat detection resources
- IDS
- Intrusion Detection System (signature based (eg. snort) or behaviour based).
- Snort/Suricata rule writing
- Host-based Intrusion Detection System (eg. OSSEC)
- SIEM
- System Information and Event Management.
- Honey pots
- Canary tokens.
- Dummy internal service / web server, can check traffic, see what attacker tries.
- Things that create signals
- Honeypots, snort.
- Things that triage signals
- SIEM
- Things that will alert a human
- Automatic triage of collated logs, machine learning.
- Notifications and analyst fatigue.
- Systems that make it easy to decide if alert is actual hacks or not.
- Examples
- Splunk.
- Arcsight.
- Qradar.
- Darktrace.
- Tcpdump.
- Wireshark.
IDS learns model of “normal” behavior, then can detect things that deviate too far from normal - eg unusual URLs being accessed, user specific- login times / usual work hours, normal files accessed.
Can also look for things that a hacker might specifically do (eg, HISTFILE commands, accessing /proc).
If someone is inside the network- If action could be suspicious, increase log verbosity for that user.
- Brute force (trying to log in with a lot of failures).
- Detecting port scanning (could look for TCP SYN packets with no following SYN ACK/ half connections).
- Antivirus software notifications.
- Large amounts of upload traffic.
- DNS queries to suspicious domains.
- HTTP headers could contain wonky information.
- Metadata of files (eg. author of file) (more forensics?).
- Traffic volume.
- Traffic patterns.
- Execution logs.
- Slow attacks are harder to detect.
- Attacker can spoof packets that look like other types of attacks, deliberately create a lot of noise.
- Attacker can spoof IP address sending packets, but can check TTL of packets and TTL of reverse lookup to find spoofed addresses.
- Correlating IPs with physical location (is difficult and inaccurate often).
Indicator of compromise (often shared amongst orgs/groups).
Host-based signatures
-
Eg changes to the registry, files created or modified.
-
Strings in found in malware samples appearing in binaries installed on hosts (/Antivirus).
Network signatures
- Eg checking DNS records for attempts to contact C2 (command and control) servers.
- dig
- Censys
- Shodan
- Whois
-
Privacy incidents vs information security incidents
-
Know when to talk to legal, users, managers, directors.
-
Run a scenario from A to Z, how would you ...
-
Good practices for running incidents
- How to delegate.
- Who does what role.
- How is communication managed + methods of communication.
- When to stop an attack.
- Understand risk of alerting attacker.
- Ways an attacker may clean up / hide their attack.
- When / how to inform upper management (manage expectations).
- Metrics to assign Priorities (e.g. what needs to happen until you increase the prior for a case)
- Use playbooks if available
-
Important things to know and understand
- Type of alerts, how these are triggered.
- Finding the root cause.
- Understand stages of an attack (e.g. cyber-kill chain)
- Symptom vs Cause.
- First principles vs in depth systems knowledge (why both are good).
- Building timeline of events.
- Understand why you should assume good intent, and how to work with people rather than against them.
- Prevent future incidents with the same root cause
- Response models
- SANS' PICERL (Preparation, Identification, Containment, Eradication, Recovery, Lessons learned)
- Google's IMAG (Incident Management At Google)
-
Evidence volatility (network vs memory vs disk)
-
Network forensics
- DNS logs / passive DNS
- Netflow
- Sampling rate
-
Disk forensics
- Disk imaging
- Filesystems (NTFS / ext2/3/4 / AFPS)
- Logs (Windows event logs, Unix system logs, application logs)
- Data recovery (carving)
- Tools
- plaso / log2timeline
- FTK imager
- encase
-
Memory forensics
- Memory acquisition (footprint, smear, hiberfiles)
- Virtual vs physical memory
- Life of an executable
- Memory structures
- Kernel space vs user space
- Tools
- Volatility
- Google Rapid Response (GRR) / Rekall
- WinDbg
-
Mobile forensics
- Jailbreaking devices, implications
- Differences between mobile and computer forensics
- Android vs. iPhone
-
Anti forensics
- How does malware try to hide?
- Timestomping
-
Chain of custody
-
Handover notes
Tell me about some recent vulnerabilities and why they caught your attention in the last six months.
Describe in as much detail as possible what happens when you type google into the address bar if your browser and hit enter
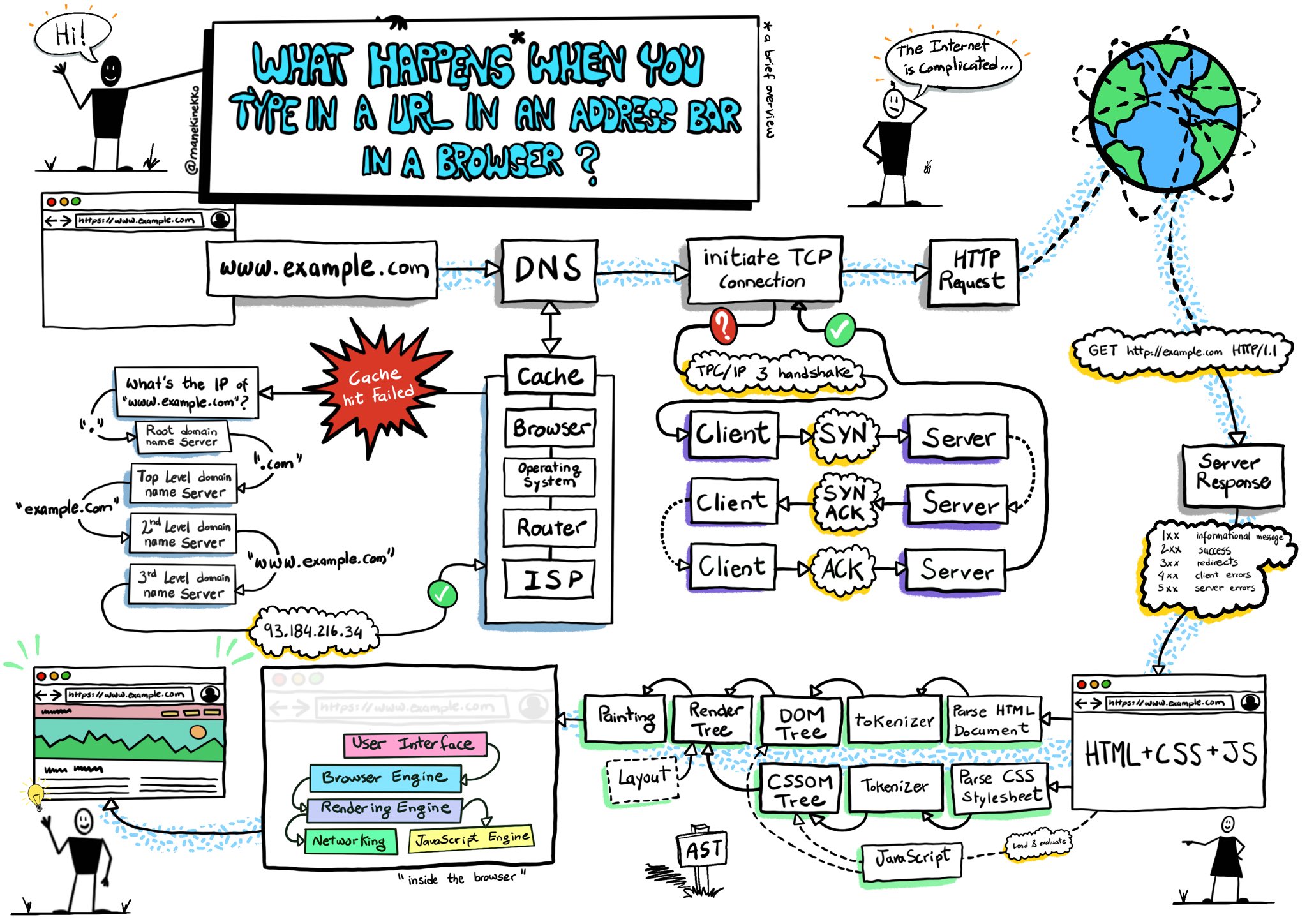
What are some common ways an attacker may move laterally throughout the network? ( stupid terms: move east/west in a network)
An act of spending time and/or effort trying to find more information or an answer or a thing.
An event will be anything that happens related to cybersecurity, incident, will be an event that may cause damage or create risk to assets.
DevOps is a methodology that combines the software development part and the technology operation part. It makes software delivering, fixing bugs and providing updates easier and faster for both developer and operator.
An investigation methodology is a framework or guidelines that gave you instruction or point you an direction at what you should do during an investigation.
Describe what I will do, what tool I will use
Example:
- First step
- Determine the severity
- CVSS Common Vulnerability Scoring System
- Assessing
- What happens?
- When?
- How?
- What did you do?
- When did you notice?
- Create the timeline
- What was the symtion?
- How many people affected?
- What is the effect / lost / impact ?
- What's the impact for doing OOXX (Shut down X system)?
- Second step
- If life & death incident > move all the living away
- Look into the logs
- Collect the logs
- Stop the incident from spreading ( contain /isolate / shutdown)
- Impact analysis / damage analysis
- Third step
- Start investigation
- Collect the logs
- Firewalls, IDS/IPS, web app, web server, server logs
- Container > docker engine logs, K8s logs
- Collect whatever is available
- Analyze the logs
- What you will do?
- If SIEM, mention the tools
- Splunk, Alienvault, Snort, Elastic Search
- Utilize the SIEM, correlate the logs
- Create the chain of events
- Find answers for Who What When Why How
- What will you first do?
- Depends on the severity of the event, I will either isolate the system or start collecting information I need.
- What will you need to do?
- I'll need to notify proper personnel who is in charge, escalate the severity of the event if needed, document every events and the time it happened.
- What info do you need?
- If possible, I'll try to collect every information that I can get. If not, I'll try to get at least the logs from security devices like IDS or SIEM and make sure they are properly timestamped.
- What’s your plan to investigate?
- I'll follow the incident response procedure that I learnt in CISSP, which is notification, escalation, reporting, system isolation, forensic analysis, evidence handling
- Who do you need to talk to?
- Manager of the security operation team, the manager of the system where the event happened, and legal counsel if required
- Ask: who do I work for?
- System owners, all the people that are impacted
- What results should you show?
- A timeline of when each events happened and how each of them are related, also provide a brief information about what the impact might be if possible
- What action has been taken, how to prevent things from happening again, find root cause to fix the problem
- How long is an investigation going to take?
- It depends on the size and the complexity of the event
- Depends on many things and how much resource do I have
- How do you know if it’s a true incident or not?
- It will be evaluated by all the actions made by the attacker along with the all the information we gathers, basically it will be determined by experience
- IoC / IoA (Indicator of Compromise / Indicator of Attack)
- Look for indicator / evidence by going through logs and SIEM
- How do you determine the chain of events happened in an incident?
- By finding some related parts in the information that we gathered, for example, a same source IP may indicates that two events are done by a same user.
- Find evidence in logs that we gathered
- What open source tools will you use to investigate an incident?
- I might be using a SIEM which can aggregate logs from different resource and virtualize the information, it will be able to help us find correlation between different log sources
- System internals (for Windows)
- Process explorer
- TCP Viewer, see open ports and activities
- Image dump, use sandbox to restore image and investigate
- What scripts will you likely write or have you written to help you investigate an incident?
- I will be writing some scripts that can identify some malicious activities and notify for me, for example, it may be finding a source IP that had sending requesting more than 10 times in a second.
- When do you consider the Investigation is done/complete?
- When we find the answer for the reason why we did this investigation, or when the cost of the investigation is exceeding the value of knowing the result of this investigation.
- When the budget time is up
- If we cannot move further > cannot find any evidence, may close the case or move to 3rd party investigation
- What do you do when the investigation is complete?
- Document everything and make sure is preserved for reference in the future if similar incidents happens
- How do you identify indicators of attack and create effective monitoring and alerting?
- Finding the root cause of the attack and see if there's any characteristic that will only appears in this type of attack, after identified the indicators of attack, I'll see if I can create firewall rules or filters to keep an eye on similar incidents that happens in the future
- What is Indicator of attacks? Name a few…
- Hash of a malware, known malicious source IP, unauthorized access attempts
- What do you do for post-mortem / lessons learned Report?
- I'll see if there's anything that we can do to help prevent similar incidents from happening again, some examples will be like firewall rules or even policy and guidelines.
- What is the root cause
Often there will be stress to investigate suspected serious security incident in a tight timeline, if you only have limited info to start with, but you are required to get this analysis done in 2 days,
- What will you plan to do for 2 days?
- I will try to set out some goals and list the tasks that need to be done then prioritize them and start with the most important tasks.
- What will you plan to deliver in 2 days?
- I will be hoping to provide at least a broad picture of the incident and also includes some direction of what future works can be done
- What if you don’t have enough info to start with?
- I will be seeking for helps from others and see if we can gather information that might be able to provide us a different view that we can start with
- What if you can’t get the report done in 2 days?
- I will provide a report of what I've done and what is currently is be doing, at the same time kept on working with the investigation
- How often will you provide update before the deadline is up?
- I will be providing updates when any of the goals are reached or tasks are done
- What resources will you need?
- I will need all the logs with timestamps of the systems and devices that are related to the incident, I might also need a help from engineers of the system who have better understand about the system and how incident like that might happens.
How do you conduct an in-depth vulnerability assessments and information system auditing of assets (e.g. servers, Workstations, Network Appliances, Storage Devices, and Applications)?
- What is the methodology?
- What info do you need to start the assessment?
- What tools do you use to conduct a vulnerability assessment?
- What are the key items you need to ask / define before starting a vulnerability assessment?
- What is considered as a vulnerability in your opinion?
- If you find a vulnerability and you are not sure if it is exploitable, what will you do?
- What is the difference between penetration testing vs Vulnerability Assessment?
- What should you include in a vulnerability assessment report?
- Example
- Ask questions:
- What is the scope?
- What do you want me to assess?
- When do you want me to do the test? Date? Time?
- Is this live system or testing system?
- Is there a backup?
- Black box? Grey box? White box?
- Rule of engagement?
- Can I do OOXX attack?
- Report example
- Executive summary
- What did I do
- When I start / end
- The scope of assess
- What test I ran
- What I found
- The servility of the things I found
- Methodology
- How did I do it
- What tools I used
- Vulnerabilities
- Description of the vulnerable
- what I found
- How to recreate the issue (include all the steps)
- If you cannot recreate it, it's not an issue
- Actual risk / actual impact
- Executive summary